Group 3-12: Transition Metals and Inner Transitional Metals (Lanthanide series and Actinide series)
- Souls of chemistry
- Jan 10, 2020
- 4 min read
Updated: Oct 2, 2020
What are Transition metals?
The transition metals are a group of metals that are found in the middle of the periodic table. They have incompletely filled d orbitals . These elements are unique as they can have an incomplete inner sub-shell allowing valence electrons in a shell other than the outer shell. Other elements only have valence electrons in their outer shell (they have valence electrons in two shells instead of only one outer shell ) This allows transition metals to form several different oxidation states. They are excellent conductors of heat and electricity. The transition metals are malleable, very hard, shiny and metallic.

Scandium(Sc):
Scandium is the first element in the third group of the periodic table. It is classified as a transition metal or rare earth metal.

Physical properties:
scandium is a silvery-white metal.
It is soft and as light as aluminum.
Chemical properties:
pure scandium reacts with acids.
It does not react with oxygen and is very resistant to corrosion.
It develops a slightly yellowish or pinkish cast when exposed to air.
once it has been ignited. It tarnished in air and burn easily.
It reacts with water to form hydrogen gas
Occurrence:
Scandium can rarely be found in nature, as it occurs in very small amounts. Scandium is usually found only in two different kinds of ores. Thortveitite is the primary source of scandium and during refining of uranium it is produced as by-product.
Uses:
It is used in color televisions.
It is used in fluorescent lamps, energy-saving lamps.
It is used in glasses and to polish glass.
The use of scandium is still growing, due to the fact that it is suited to produce catalysers.
It is used in aluminium-scandium alloys for the aerospace industry and for sports equipment (bikes, baseball bats, etc.) which rely on high performance materials.
Discovery:
It was discovered by Lars Nilson in 1879 . He extracted it from mineral
euxenite and gadolinite and named scandium after his homeland using the Latin word "Scandia" which stood for "Scandinavia".
Fascinating facts:
It has thirteen radioisotopes.Most of scandium's radioactive isotopes have half-lives of less than two minutes.
It is combined with aluminum into an alloy used for high-performance equipment, especially by the aerospace industry.
Titanium(Ti):
Titanium is the first element in the fourth group of the periodic table. It is classified as a transition metal.

Physical properties:
It is strong, lustrous, corrosion-resistant.
It is silvery white light metal.
Chemical properties:
Pure titanium is not soluble in water but is soluble in concentrated acids. This metal forms a passive but protective oxide coating (helps in corrosion-resistance) when exposed to elevated temperatures in air.
at room temperature it resists tarnishing.
It reacts in a similar way with hot concentrated acids,
Occurrence:
Titanium is not found as a pure element in nature, but is found in compounds as part of minerals in the Earth's crust. The most important minerals for mining titanium are rutile and ilmenite. The top producing countries of these ores are Australia, South Africa, and Canada.
Uses:
The titanium dioxide is extensively used as a white pigment in outside paintings for being chemically inert, for its great coating power, its opacity.
Titanium alloys are having high tensile strength even at high temperatures, light weight and high corrosion resistance.
As it can withstands with extreme temperatures. due to these properties they are principally used in aircraft, pipes for power plants, armour plating, naval ships, spacecraft and missiles.
In medicine titanium is used to make hip and knee replacements, pace-makers, bone-plates and screws and cranial plates for skull fractures.
Discovery:
It is discovered by William Gregor in 1791. Titanium gets its names from the Titans who were Greek gods.
Fascinating facts:
Titanium is as strong as steel but very lighter.
Titanium containers are used to store nuclear waste.
Vanadium(V):
Vanadium is the first element in the fifth group of the periodic table. It is classified as a transition metal.

Physical properties:
vanadium is a hard, silvery metal.
It is very ductile, malleable, and resistant to corrosion.
Chemical properties:
Vanadium does not react with water or oxygen at room temperature.
Many vanadium compounds are considered toxic.
Occurrence:
Vanadium is found in a wide variety of minerals in the Earth's crust. Some minerals containing vanadium include vanadinite, carnotite, and magnetite. The majority of vanadium production comes from magnetite.
Around 98% of the vanadium ore that is mined is in South Africa, Russia, and China.
Uses:
Vanadium with aluminium in titanium alloys is used in jet engines and high speed air-frames.
It is in steel alloys are used in axles, gears and other critical components.
Vanadium alloys are also used in nuclear reactors because vanadium has low neutron-adsorption abilities and it doesn not deform under high temperatures.
Vanadium oxide (V2O5) is used as a catalyst in manufacturing sulfuric acid and maleic anhydride and in making ceramics.
It is added to glass to produce green or blue tint. Glass coated with vanadium dioxide (VO2) can block infrared radiation at some specific temperature.
Discovery:
It is discovered by Nils Sefstrom in 1830. He gave Vanadium its name from the Scandinavian goddess of beauty "Vanadis".
Fascinating facts:
It has very colorful oxidation states including purple (+2), green (+3), blue (+4), and yellow (+5).
Most of the vanadium (about 80%) produced is used as a steel additive.
Coming soon..........
Chromium(Cr):

Manganese(Mn):

Iron(Fe):

Cobalt(Co):

Nikel(Ni):

Zinc(Zn):

Silver(Ag):
Platinum(Pt):
Gold(Au):
Mercury(Hg):
Inner Transitional Metals
Lanthanide series:
Lanthanide series, is a series of rare-earth metallic elements. These are the elements with unfilled f orbitals. Lanthanides are all metals with reactivity similar to group 2 elements. Lanthanides are used in optical devices (night vision goggles), petroleum refining, and alloys.
Cerium(Ce):

Physical properties:
Chemical properties:
Occurrence:
Uses:
Discovery:
Fascinating facts:
Praseodymium(Pr):

Physical properties:
Chemical properties:
Occurrence:
Uses:
Discovery:
Fascinating facts:
Neodymium(Nd):

Physical properties:
Chemical properties:
Occurrence:
Uses:
Discovery:
Fascinating facts:
Coming soon..........
Promethium:
Samarium:
Europium:
Gadolinium:
Terbium:
Dysprosium:
Holmium:
Erbium:
Thulium:
Ytterbium:
Lutetium:
Actinide series:
Actinides are all radioactive elements. these are elements with unfilled f orbitals. Actinides are found primarily in applications where their radioactivity can be used to power devices such as cardiac pacemakers.
Thorium(Th):

Physical properties:
Chemical properties:
Occurrence:
Uses:
Discovery:
Fascinating facts:
Protactinium(Pa):

Physical properties:
Chemical properties:
Occurrence:
Uses:
Discovery:
Fascinating facts:
Uranium(U):

Physical properties:
Chemical properties:
Occurrence:
Uses:
Discovery:
Fascinating facts:
Neptunium(Np):

Physical properties:
Chemical properties:
Occurrence:
Uses:
Discovery:
Fascinating facts:
Plutonium(Pu):
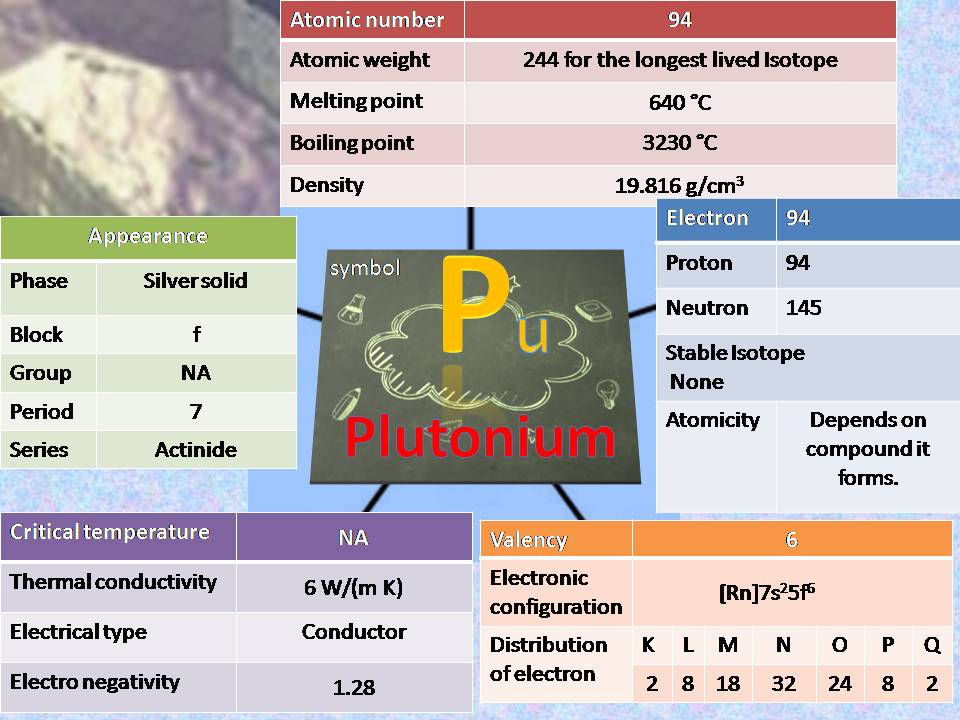
Physical properties:
Chemical properties:
Occurrence:
Uses:
Discovery:
Fascinating facts:
Americium(Am):

Physical properties:
Chemical properties:
Occurrence:
Uses:
Discovery:
Fascinating facts:
Curium(Cm):


I want to ask permission to save a picture of the iron section notes. tq